Data provider
Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department of Applied Biotechnology and Food Science, Environmental Microbiology and Biotechnology Group
Contact details
Compulsory sheet of the technology
Financing of the project
Application sphere
- Metals, semi-metals and their compounds
- cadmium
Description of environmental risk
- Metals, semi-metals and their compounds
- copper
Description of environmental risk
- Metals, semi-metals and their compounds
- nickel
Description of environmental risk
- Metals, semi-metals and their compounds
- zinc
Description of environmental risk
- Metals, semi-metals and their compounds
- lead
Description of environmental risk
- Metals, semi-metals and their compounds
- chromium
Description of environmental risk
- Petroleum derivatives (TPH)
- TPH (total)
Description of environmental risk
Information on the technology
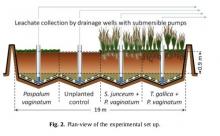
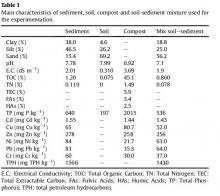
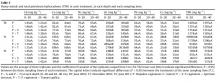
A technológia során egy fitoremediációs kísérletet hoztak létre, melynek az volt a célja, hogy magas iszap-agyag frakcióval, magas sótartalommal rendelkező kikotort tengeri üledékeket kezeljenek és mérsékeljék a nehézfémek és szerves szennyezők okozta szennyezettséget. A fitoremediáció során egy szennyezett környezetet növények segítségével tisztítanak meg. Négy különböző kezelést választottak ki, ebből háromnál különböző növényeket alkalmaztak, ezeket összehasonlították egymással valamint a kontrollal. A növények termőképességét vizsgálták az üledékekben. A monitoring egy évig tartott, ennek leteltével a hidrolitikus enzim és a dehidrogenáz aktivitás növekedése jelezte az üledék serkentő funkcionálisságát. Az alkalmazott növények hatásosak voltak a szennyezett tengeri üledékek mindkét szerves és a szervetlen szennyezőktől történő tisztításában. A növények hatékonyan csökkentették az üledék sótartalmát, szerves szennyezőanyag tartalmát és nehézfémtartalmát is. A TPH értéke magas volt a kezelés kezdetekor, de a kezelés ezt a mennyiséget is csökkentette. A szerves szennyezőknek a lebontása a komposzt alkalmazásának és a mikrobiális tevékenység serkentő hatásának köszönhető. A mikroorganizmusok adszorpciója csökkentheti az alkalmazkodási idejüket és növeli a lebontás hatásfokát.
A kikotort üledék fitoremediációja még egy új technológiának tekinthető ami további vizsgálatokat igényel ahhoz, hogy kimutathassa a hatékonyság szintjét. Növényekkel történő tengeri üledék remediációja.A kísérletben komposzt hozzáadásával vizsgálták a növények termőképességét az üledékekben.
Technology classification
- phytoremediation
- phytoextraction based soil remediation
Technology-monitoring
elektromos vezetőképesség
Costs of the technology
SWOT (evalaution based on scores)
SWOT (evaluation in words)
A technológiával tisztíthatók a tengeri üledékek, eltávolíthatóak a nehézfém és szerves szennyezőanyagok, valamint javítható az üledékek kémiai, fizikai és biokémiai tulajdonsága. A kezelés során a fémek nem tudtak mozogni a felső réteg felől a mélyebb rétegek felé esőzés és öntözés hatására.
A szennyezőanyagot kinyert növényeket kezelni kell. A folyamat idő- és helyigényes. Csak a kezelés helyszínéről irányíthatóak a folyamatok. Az ex situ alkalmazás az üledék eltávolítását igényli.
A technológia más szennyezőanyagok eltávolítására is alkalmas lehet.
Az üledék biológiailag elérhető frakcióját is figyelembe véve megállapítható lehet a nehézfémek anyagmérlege. A biomolekuláris módszerek alkalmazását is figyelembe véve azon mikroorganizmusok azonosítása lenne megoldott melyeknek jelentős szerepe van az üledék remediációjában.
Completed applications
Size of the treated area
Publications, references
Masciandaro, G., Ceccanti, B., Ronchi, V., Bauer, C., 2000. Kinetic parameters of
dehydrogenase in the assessment of the response of soil to vermicompost and inorganic fertilisers. Biol. Fertil. Soils 32, 479-483.
King, R.F., Royle, A., Putwain, P.D., Dickinson, N.M., 2006. Changing contaminant
mobility in a dredged canal sediment during a three year phytoremediation trial. Environ. Pollut. 143, 318-326.