Data provider
Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department of Applied Biotechnology and Food Science, Environmental Microbiology and Biotechnology Group
Contact details
Compulsory sheet of the technology
Financing of the project
Application sphere
- Chemical soil degradation
- Other
Description of environmental risk
- Chemical soil degradation
- Other
Description of environmental risk
- Chemical soil degradation
- Other
Description of environmental risk
- Other soil degradation
- Other
Description of environmental risk
- Other soil degradation
- Other
Description of environmental risk
- Other soil degradation
- Other
Description of environmental risk
- Other soil degradation
- Other
Description of environmental risk
- Other soil degradation
- Other
Description of environmental risk
Information on the technology
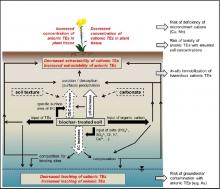
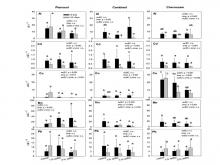
Faforgácsból készül bioszénnel történő kezelési technológiát alkalmaztak 3 különböző talajtípusra (Planosol/homokos vályog, Cambisol/agyagos vályog, Chernozem/iszapos vályog). Megvizsgálták, hogy a faforgács bioszén milyen hatással van a talaj, a talajból összegyűjtött csurgalékvíz és a talajokba ültetett mustár növényre, azok fizikai illetve kémiai paramétereire. Minden talajtípusnál kontroll mintát, illetve 1% és 3% (w/w) bioszénnel kezelt talajokat vontak be a vizsgálatba. A talajmintákat 0 és 7 hónappal a kísérlet kezdete után vették, a csurgalékvíz mintákat pedig a 0. és az 54. napon gyűjtötték be.
Természetes anyag használata talajjavításra, ugyanis a technológia faaprítékból készült bioszenet használ.
Technology classification
- Soil amelioration with biochar
- Soil amelioration with biochar from agricultural and forestry waste
Technology-monitoring
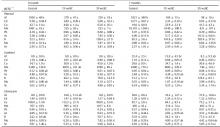
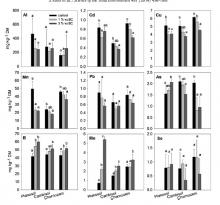
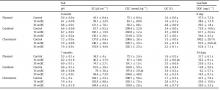
Al, Cd, Cu, Mn, Pb, As, B, Mo, Se,
EC, OC, DOC, növény által felvett fémtartalom
Costs of the technology
Figyelembe vettem, hogy a kísérlet időtartama 7 hónap , és a szilárd talajminták mérése ICP-MS-sel történt.
SWOT (evalaution based on scores)
SWOT (evaluation in words)
Viszonylag könnyen kialakítható és mérhető technológia, minimális energiaigény kell, nincsenek nagyobb költségek és munkagépek sem kellenek, túlzott emberi beavatkozást sem igényel, csak a fenntartásra kell figyelni. A technológia során a veszélyhelyzetek minimálisak. Sokoldalú javítási lehetőséget jelent, többféle talajban.
A nyomelemet kinyert növényt kezelni kell. A folyamat időigényes, ha eredményt akarunk felmutatni. Nem túl hatékony, kis koncentrációkat mozgat meg ez a technológia. Mindazonálltal, hogy nem túl bonyolult a technológia, odafigyelést igényel, a kezelni kívánt talajhoz kell igazítani, annak függvényében, hogy mit milyen paraméteren szeretnénk javítani.
A technológia szennyezőanyagok eltávolítására és talajjavításra is alkalmas.
A kationos nyomelemek mennyisége a csurgalékvízben lecsökken, az anionos nyomelemeké pedig megnövekedik.
Completed applications
Size of the treated area
- Agricultural
Publications, references
Stefanie Kloss , Franz Zehetner , Eva Oburger, Jannis Buecker, Barbara Kitzler, Walter W. Wenzel, Bernhard Wimmer, Gerhard Soja: Trace element concentrations in leachates and mustard plant tissue (Sinapis alba L.) after biochar application to temperate soils, Science of the Total Environment 481 (2014) 498–508
Stefanie Kloss , Franz Zehetner , Eva Oburger, Jannis Buecker, Barbara Kitzler, Walter W. Wenzel, Bernhard Wimmer, Gerhard Soja: Trace element concentrations in leachates and mustard plant tissue (Sinapis alba L.) after biochar application to temperate soils, Science of the Total Environment 481 (2014) 498–508